Scholarships for High School Seniors
Scholarships for high school seniors represent a crucial stepping stone towards higher education, offering financial relief and opening doors to countless opportunities. Securing funding for college can feel daunting, but understanding the various scholarship types, application processes, and strategies for increasing your chances significantly improves your prospects. This guide navigates the landscape of high school senior scholarships, providing valuable insights and practical advice to help you achieve your academic aspirations.
From merit-based awards recognizing academic excellence to need-based grants assisting students facing financial hardship, the options are diverse. We’ll explore the different types of scholarships, effective search strategies, and the key components of a compelling application, including crafting a strong essay and tailoring it to each scholarship’s unique requirements. We will also discuss the importance of exploring additional financial aid options and creating a realistic timeline for applications. Ultimately, securing scholarships is a strategic process that combines diligent research, effective planning, and a clear understanding of your strengths and goals.
Types of Scholarships for High School Seniors
Securing funding for higher education is a significant step for many high school seniors. A variety of scholarships exist, each with its own eligibility criteria and application process. Understanding these different types can greatly increase your chances of finding and securing financial aid.
Merit-Based and Need-Based Scholarships
Merit-based scholarships reward academic achievement, talent, or other exceptional qualities. Need-based scholarships, conversely, are awarded based on demonstrated financial need. The key difference lies in the selection criteria: merit focuses on achievement, while need focuses on financial circumstances. A student with a high GPA might qualify for a merit-based scholarship, while a student from a low-income family might qualify for a need-based one. Some scholarships even combine both merit and need criteria, requiring a minimum GPA alongside a financial need assessment.
Types of Scholarships Categorized
The following table provides a categorized list of scholarship opportunities available to high school seniors. Knowing these categories can help you target your search effectively.
| Category | Description | Eligibility Criteria | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Merit-Based | Awarded based on academic achievement, talent, or other exceptional qualities. | High GPA, standardized test scores, leadership roles, extracurricular activities. | National Merit Scholarship |
| Need-Based | Awarded based on demonstrated financial need, often determined through the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid). | Low family income, significant financial burden for college. | Pell Grant (federal need-based grant) |
| Specific Talent/Skill-Based | Awarded based on specific skills or talents, such as artistic ability, athletic prowess, or musical talent. | Demonstrated proficiency in a particular area, often through auditions, portfolios, or competitions. | Athletic scholarships offered by universities |
| Community-Based | Offered by local organizations, businesses, or community groups within a specific geographic area. | Residency requirements, involvement in community activities. | Local Rotary Club scholarships |
| Major-Specific | Awarded to students intending to pursue a specific field of study. | Declared major, interest in the specific field. | Engineering scholarships from specific companies |
| Minority-Based | Aimed at supporting students from underrepresented minority groups. | Membership in a specific minority group. | Scholarships specifically for Hispanic students |
Scholarship Application Processes
The application process for scholarships varies but typically involves several key steps: researching available scholarships, gathering required documents (transcripts, letters of recommendation, essays), completing the application forms accurately and thoroughly, and submitting the application by the deadline. Many applications require essays detailing personal experiences, goals, and aspirations, showcasing the applicant’s personality and suitability for the scholarship. Strong letters of recommendation from teachers, counselors, or other mentors are often crucial components of a successful application. Thorough proofreading and careful attention to detail are essential throughout the entire process.
Finding Scholarship Opportunities
Securing financial aid for college is a crucial step for many high school seniors. The sheer number of scholarships available can feel overwhelming, but with a strategic approach, you can significantly increase your chances of finding and winning funding. This section provides resources and a structured approach to your scholarship search.
Finding the right scholarships requires diligent research and a well-defined strategy. Utilizing reputable websites and employing effective search techniques will maximize your success.
Reputable Scholarship Websites and Resources
Many reliable online platforms offer extensive databases of scholarships. Leveraging these resources significantly increases your chances of finding suitable opportunities. Remember to always verify the legitimacy of any scholarship before applying.
- Fastweb: A popular website featuring a vast database of scholarships, grants, and internships. It uses a user-friendly interface with customizable search filters.
- Scholarships.com: Another comprehensive resource with a wide array of scholarships categorized by criteria such as major, GPA, and ethnicity.
- College Board: This well-known organization provides access to numerous scholarships and financial aid resources, often linked directly to specific colleges and universities.
- Peterson’s: Similar to Fastweb and Scholarships.com, Peterson’s offers a large database searchable by various criteria, including academic merit and extracurricular achievements.
- Your High School Guidance Counselor: Your school counselor is an invaluable resource, possessing knowledge of local and school-specific scholarships that may not be listed online.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Searching for Scholarships
A systematic approach is key to effectively navigating the scholarship search process. Following these steps will help you focus your efforts and maximize your results.
- Assess your qualifications: Identify your strengths, including GPA, academic achievements, extracurricular activities, and community involvement. This will help you target scholarships that align with your profile.
- Define your search criteria: Determine your priorities. Are you looking for scholarships based on major, location, ethnicity, or specific talents? Narrowing your focus will save time and effort.
- Utilize multiple search platforms: Don’t rely on a single website. Explore several reputable resources to broaden your search and increase your chances of finding suitable opportunities.
- Use targeted keywords: Employ specific keywords in your searches. For example, instead of “scholarship,” try “engineering scholarship for women” or “music scholarship for California residents.”
- Refine your search results: Use the filtering options available on each website to narrow down the results based on your specific criteria (e.g., GPA requirements, deadline, award amount).
- Keep track of deadlines: Maintain an organized list of scholarships and their deadlines to ensure you don’t miss any opportunities. Use a calendar or spreadsheet to manage your applications.
- Review application requirements carefully: Before applying, thoroughly review each scholarship’s requirements to ensure you meet all criteria and can submit a strong application.
Sample Search Strategy
Let’s say a student is majoring in biology, has a 3.8 GPA, and resides in Texas. Their search strategy could involve the following:
Search terms: “biology scholarship Texas,” “Texas biology scholarship 3.8 GPA,” “undergraduate biology scholarship Texas,” “biology merit scholarship Texas.”
They would utilize the filtering options on each website to refine their results based on GPA, location (Texas), and major (biology). They would also consider scholarships related to specific areas within biology, such as environmental science or genetics, to further narrow their search. They would then prioritize scholarships with deadlines further in the future, allowing more time for a strong application.
The Scholarship Application Process
Navigating the scholarship application process can feel overwhelming, but understanding the common components and strategies for a successful application will significantly increase your chances of securing funding for your higher education. This section outlines the key elements of most scholarship applications and provides guidance on crafting compelling submissions.
The scholarship application process typically involves several key components. Each application will have its own specific requirements, but generally, you can expect to encounter the following:
Common Application Components
A strong application demonstrates not only academic achievement but also personal qualities and future goals. The components work together to paint a comprehensive picture of the applicant. A well-rounded application shows a commitment to detail and a genuine interest in the scholarship opportunity.
Essays: These are crucial for showcasing your personality, experiences, and aspirations. They provide a platform to articulate your unique qualities and demonstrate how you align with the scholarship’s values and goals. A strong essay is well-written, focused, and engaging. A weak essay often lacks focus, contains grammatical errors, and fails to connect the applicant’s experiences to the scholarship’s purpose.
Examples of Strong and Weak Scholarship Essays
Here are examples to illustrate the differences:
Strong Essay Example: “My passion for marine biology ignited during a childhood summer spent exploring tide pools. Witnessing the intricate ecosystem firsthand fueled my desire to understand the delicate balance of our oceans. This experience, coupled with my academic achievements in AP Biology and my volunteer work at the local aquarium, has solidified my commitment to pursuing a career in marine conservation. The [Scholarship Name] scholarship would not only provide invaluable financial support but also allow me to connect with a community of like-minded individuals, furthering my dedication to protecting our planet’s precious resources.”
Weak Essay Example: “I want a scholarship because college is expensive. I like science and want to be a doctor. I got good grades. I hope you pick me.”
Tailoring Applications to Specific Requirements
Each scholarship has unique criteria and priorities. Generic applications rarely succeed. Carefully review the scholarship guidelines and tailor your application to directly address the specific requirements and demonstrate how your qualifications and aspirations align with the organization’s mission and values. This includes customizing your essay to reflect the specific interests and priorities of the scholarship provider, highlighting relevant experiences and skills, and ensuring your application materials directly respond to the specific questions or prompts provided. For example, if a scholarship focuses on community service, emphasize your volunteer experiences and their impact. If it emphasizes leadership, highlight your leadership roles and accomplishments. Thoroughly researching the organization and tailoring your application accordingly significantly increases your chances of success.
Financial Aid and Scholarships
Securing funding for higher education is a crucial step in the college application process. Understanding the different types of financial aid available, their sources, eligibility requirements, and repayment terms is essential for making informed decisions. This section will compare and contrast scholarships with other forms of financial aid, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each, and emphasizing the importance of completing the FAFSA.
Comparison of Financial Aid Types
Choosing the right financial aid option significantly impacts a student’s financial future. The following table provides a comparison of scholarships, grants, and loans, illustrating key differences in their source, eligibility criteria, and repayment requirements.
| Aid Type | Source | Eligibility | Repayment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scholarship | Colleges, universities, private organizations, corporations, and individuals | Varies widely; based on academic merit, athletic ability, financial need, demonstrated talent, community involvement, or other criteria. | None; it’s free money. |
| Grant | Federal and state governments, colleges, and private organizations | Typically based on financial need, as determined by the FAFSA. Some grants are merit-based. | None; it’s free money. |
| Loan | Federal and private lenders | Generally based on creditworthiness (for private loans) or financial need (for federal loans). | Requires repayment with interest, typically beginning after graduation or leaving school. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Scholarships vs. Loans
Relying on scholarships versus loans for college funding presents distinct advantages and disadvantages. Scholarships offer the benefit of free money, reducing or eliminating the need for debt after graduation. However, securing scholarships is often competitive, and the availability of scholarships may not fully cover the cost of education. Loans, on the other hand, provide a more reliable source of funding, but come with the burden of repayment, potentially impacting future financial stability. A strategic approach might involve a combination of scholarships and loans to minimize debt while ensuring sufficient funding for college.
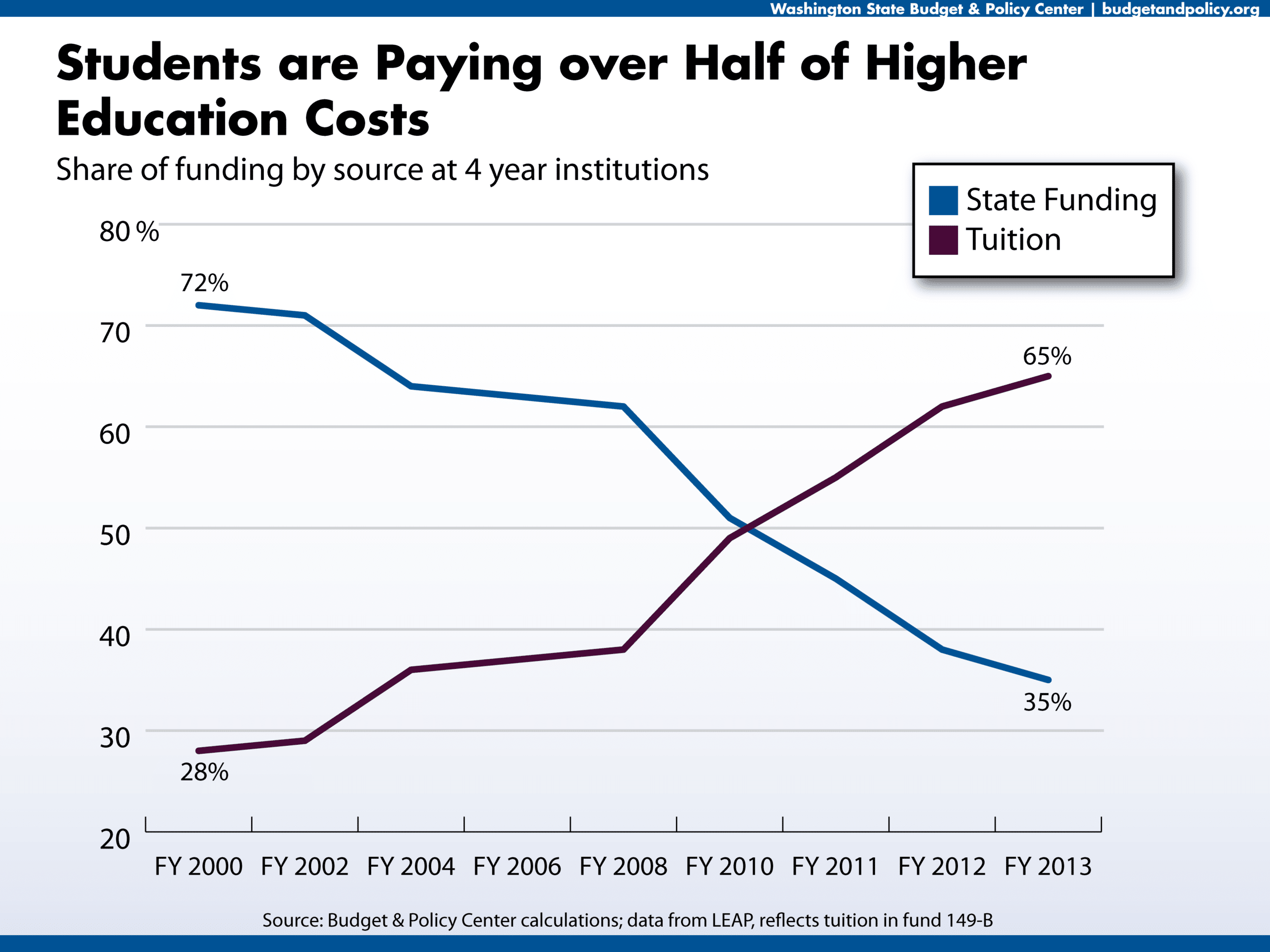
Importance of Completing the FAFSA
Completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is paramount for accessing federal student aid, including grants and loans. Many colleges and universities also use FAFSA information to determine eligibility for institutional aid, including scholarships. The FAFSA provides a standardized measure of financial need, making it a crucial component of the financial aid application process. Failing to complete the FAFSA could significantly limit a student’s access to financial aid opportunities. Furthermore, some scholarships require applicants to have completed the FAFSA as a prerequisite for consideration. Therefore, completing the FAFSA is a critical first step in securing financial aid for college.
Strategies for Increasing Scholarship Chances
Securing scholarships requires a multifaceted approach. While academic merit plays a significant role, a holistic presentation of your achievements and aspirations significantly enhances your chances. This section outlines effective strategies to improve your competitiveness in the scholarship application process.
A strong application demonstrates not only academic excellence but also a well-rounded individual with diverse interests and a clear vision for the future. Focusing on a combination of high GPA, meaningful extracurricular activities, and impactful volunteer work creates a compelling narrative that resonates with scholarship committees.
High GPA and Academic Excellence
Maintaining a high grade point average (GPA) is foundational to securing scholarships. A strong academic record showcases dedication, discipline, and the ability to excel in challenging coursework. Many scholarships specifically target high-achieving students, often setting minimum GPA requirements. Beyond simply achieving high grades, demonstrating consistent improvement throughout high school is equally important. For example, a student who consistently raises their GPA each year showcases growth and perseverance, which are valuable qualities. Supplementing high grades with challenging coursework, such as Advanced Placement (AP) or International Baccalaureate (IB) classes, further strengthens your application.
Extracurricular Activities and Leadership Roles
Participation in extracurricular activities demonstrates well-roundedness, leadership potential, and commitment beyond academics. Scholarship committees look favorably upon students involved in activities that showcase teamwork, dedication, and a passion for something beyond the classroom. Leadership roles within these activities are particularly impactful, highlighting your ability to organize, motivate, and guide others. Examples include serving as captain of a sports team, president of a club, or leading a community project. The quality of your involvement is more important than the sheer quantity. Deep engagement and demonstrable impact within a few activities are more effective than superficial involvement in many.
Volunteer Work and Community Service
Demonstrating a commitment to community service through volunteer work is highly valued by scholarship committees. It shows a dedication to helping others and contributing to society. Choose volunteer experiences that align with your interests and values. For example, a student passionate about environmental conservation might volunteer at a local nature center, while a student interested in healthcare might volunteer at a hospital. Clearly articulate the impact of your volunteer work in your application. Quantify your contributions whenever possible; for example, instead of saying “I volunteered at a food bank,” say “I volunteered 100 hours at a local food bank, assisting in sorting and distributing food to over 500 families.”
Scholarship Application Timeline
Creating a well-organized timeline is crucial for successfully navigating the scholarship application process. This sample timeline provides a framework; adjust it based on specific scholarship deadlines.
| Month | Task |
|---|---|
| September – October | Research scholarship opportunities; begin brainstorming essay topics. |
| November – December | Finalize essay drafts; request letters of recommendation. |
| January – February | Complete and submit applications; track deadlines. |
| March – April | Follow up on applications; prepare for potential interviews. |
| May – June | Await notification of awards. |
Building a Compelling Narrative
Scholarship applications are not simply a list of achievements; they are opportunities to tell your story. Crafting a compelling narrative that showcases your unique achievements and aspirations is essential. Begin by identifying your key strengths and experiences. Then, weave these elements into a cohesive story that highlights your personality, values, and goals. Focus on specific examples that illustrate your qualities. For instance, instead of stating “I am a hard worker,” describe a specific situation where your hard work led to a significant accomplishment. Use strong verbs and vivid language to create an engaging narrative that captures the attention of the scholarship committee. Conclude with a clear articulation of your future aspirations and how the scholarship will help you achieve them.
Post-Acceptance Considerations
Securing a scholarship is a significant achievement, but the process doesn’t end with notification. Careful consideration of the offer and its implications is crucial for maximizing its benefits and making informed decisions about your college journey. Understanding the acceptance and declination procedures, as well as the scholarship’s potential impact on your college choices, will ensure a smooth transition into higher education.
The process of accepting or declining a scholarship offer typically involves a formal response to the awarding institution. This often entails completing an online form, submitting signed paperwork, or replying via email, depending on the scholarship provider’s instructions. Deadlines for acceptance are usually strict, so promptly reviewing the terms and conditions, including any required actions, is vital. Failure to respond within the stipulated timeframe may result in forfeiture of the award. Conversely, declining a scholarship should also be done formally, often through the same channels used for acceptance. While disappointing to forgo funding, a formal declination maintains professional courtesy and allows the institution to offer the scholarship to another deserving candidate.
Scholarship Acceptance and Declination Procedures
Accepting a scholarship usually involves completing an online acceptance form, often requiring confirmation of enrollment at the designated institution. Some scholarships may also require additional documentation, such as proof of enrollment or transcripts. Deadlines for acceptance are strictly enforced; missing the deadline typically forfeits the award. Declining a scholarship generally involves a formal notification to the awarding institution, often through a similar online form or email. While disappointing, a timely and formal declination is crucial for maintaining professionalism and allowing the scholarship to be offered to another student. It’s always advisable to keep records of all communication and confirmations related to scholarship acceptance or declination.
Impact of Scholarships on College Choices
Receiving a scholarship can significantly influence your college selection. A substantial scholarship offer from a less-preferred college might outweigh the appeal of a more desirable institution without significant financial aid. For example, a full-ride scholarship to a state college could be more financially advantageous than attending a prestigious private university with only partial financial aid. Conversely, a smaller scholarship at a preferred university might still be a worthwhile option if the overall cost, including tuition, fees, and living expenses, is manageable. It’s essential to weigh the financial benefits against factors such as academic program quality, location, and campus culture when making your final decision. Creating a detailed cost comparison sheet for each college, including tuition, fees, room and board, and other expenses, alongside the scholarship amounts received, will greatly aid in this decision-making process.
Post-Scholarship Award Checklist
After receiving a scholarship, a systematic approach is crucial to ensure all necessary steps are taken. This involves confirming the terms and conditions of the award, understanding the disbursement schedule, and addressing any further requirements set by the awarding institution.
A detailed checklist should include:
- Carefully review the scholarship agreement to understand all terms and conditions.
- Confirm the disbursement schedule and payment method.
- Maintain regular communication with the scholarship provider regarding any updates or requirements.
- Understand and adhere to any academic requirements or reporting obligations.
- Keep copies of all scholarship-related documents, including acceptance letters, agreements, and payment confirmations.
- If applicable, inform your college financial aid office about the scholarship award.
Closing Summary
Successfully navigating the scholarship application process requires dedication and a strategic approach. By understanding the different types of scholarships available, employing effective search techniques, and crafting compelling applications, high school seniors can significantly increase their chances of securing financial aid for college. Remember to start early, research thoroughly, and present yourself authentically to showcase your unique talents and aspirations. The rewards of securing scholarships extend beyond financial assistance; they provide a sense of accomplishment and validation, setting the stage for a successful college journey and beyond.